Reduced workweek from the traditional 5-day work week to a 4-day work week have found many benefits, the idea of working four days a week have attracted many companies and organization around the globe to implementing the new four-day workweek arrangement.
Here’s a question for you, “Do you know what does a four-day work week actually means?”
KEY TAKEAWAY
- The two main 4-day work week model are 4/10 Work Week Model (100% pay and productivity for 80% of the time) and 4/8 Work Week Model (100% pay and productivity for longer working hours and less working days).
- Employees suited for the 4/10 Work Week Model are hourly wages workers and people facing professionals, while employees suited for the 4/8 Work Week Model are executive and people manager or task-oriented professionals.
- Studies shows on average, only 37% of the time are spend working on activities that make a difference in the team or organization’s success, while 63% of the time are spent on unproductive work.
What Is A 4 Day Work Week?
A 4 day work week is a work schedule in which full-time employees work four days per week instead of the traditional five, while being paid 100% of the salary in exchange for a commitment to maintain at least 100% productivity.
By adjusting the labor days, shortening the work week, companies can create an improved working environment where hours of each day are used more effectively.
“A 4-day work week is to achieve the same results with 20% less working time.”
Antony, Founder of HQHIRE
With fewer days of a week spent working, employees will be given a work environment that allows them to feel a greater purpose in life and better work-life balance.
Models of 4-Day Work Week
There are two main models of a 4-Day work week. As a 4-day work week is a fairly new concept, and there is no consensus on how each 4-day work week model is named.
At HQHIRE we have named the different Models of 4-Day Work Week according to what it actually does for easy understanding.
- 4/10 Work Week Model: 4 Days of work, 10 hours per day.
- 4/8 Work Week Model: 4 Days of work, 8 hours per day.
4/10 Work Week Model: 40 Hours Work Week
Employees work at a compressed work schedule for 4 days, with each day working 10 hours instead of the traditional 8 hours. On average employees who work on a 4/10 work week (“Four-Ten”) will work a total of 38 to 40 hours each week, working 4 days a week.

Pros of the 4/10 Work Week Model
- No change in the number of hours each employee works each week.
- Hourly employees can benefit from working 4 days a week without reducing of income.
- Paid the same wage as traditional 5-day work week employees.
- Employees are able to enjoy working 4 days a week.
Cons of the 4/10 Work Week Model
- Intense working hours that are comparable to shift workers.
- 5 days’ worth of work crammed into 4 days.
- Long working hours may lead to burnout of employees.
- Employees will less likely choose to work overtime even when required.
With the 4/10 work week model, employees work longer work shifts each day, with no change in the total number of hours worked by each employee when compared to the traditional 5-day work week.
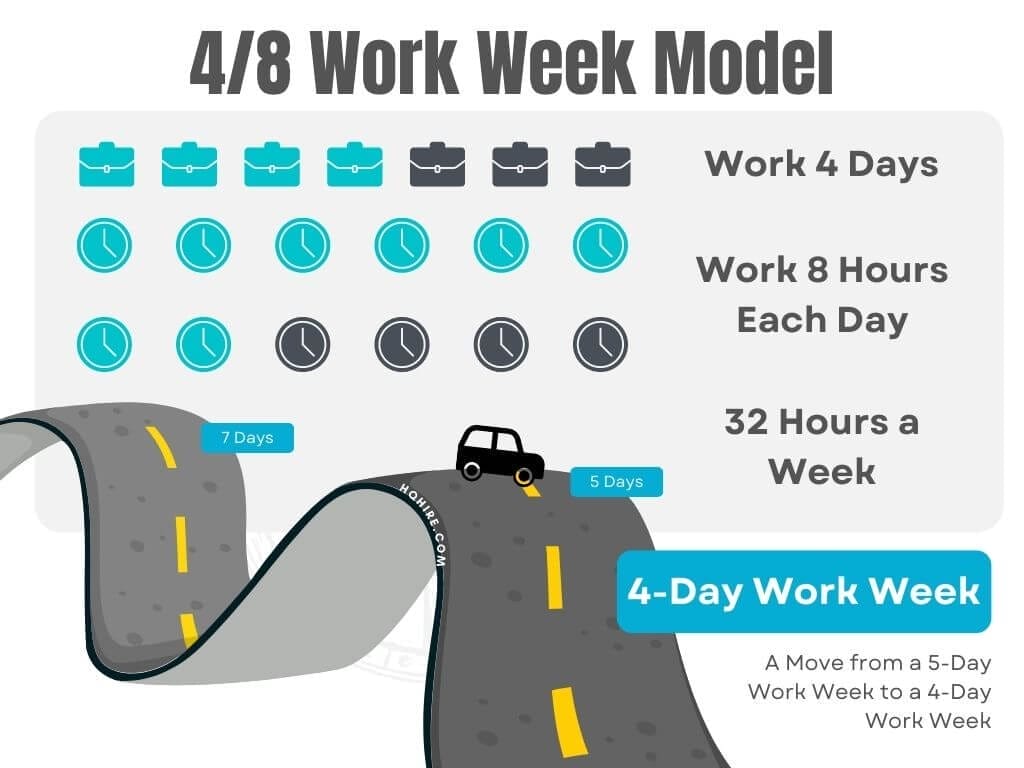
4/8 Work Week Model: 32 Hours Work Week
Employees work for 4 days, with the same number of hours worked each day and a total of fewer hours of work each week. On average employees who work on a 4/8 Work Week (“Four-Eight”) will spend a total of 30 to 32 hours at work each week, working 4 days a week.
Pros of the 4/8 Work Week Model
- Less overall work hours each week.
- Employees are given extra time to rest and rejuvenated from the daily work stress, which prevents employees from being burnout at work.
- Improve employees’ well-being which motivated employees to innovate and make work more effective and be more productive at work.
- Lower turnover rate and great job satisfaction.
- Paid the same wage as traditional 5-day work week employees.
- Employees are able to enjoy working 4 days a week.
Cons of the 4/8 Work Week Model
- Hourly wage workers may lead to a lower income.
- Reducing working hours doesn’t mean reducing the amount of work.
- Work needs to be performed at least 20% more effectively.
- Employees may choose to perform overtime, especially when work is not able to perform more effectively.
With the 4/8 work week model, employees achieve the same level of the result of a 5-day work week with a 20% increase in work efficiency each day.
A 4-day work week is achieved by improvement of the process and reduction of the unproductive hours at work.
Which 4-Day Work Week Model is Better?
The different four-day work week models; the 4/10 Work Week Model and the 4/8 Work Week Model each have their pros and cons. Depending on each industry, companies can adapt to the different four-day work week models that can benefit both the employee and the employer.
The four-day work week has been shown to improve work productivity and well-being for employees which helps to retain talents and reduce business operational costs.
Employees suited for the 4/10 Work Week Model
- Hourly wages worker
- People facing professions
Employees suited for the 4/8 Work Week Model
- Executive and people manager
- Task-oriented professions
Careful planning of the operational changes can help both the employer and the employee in transiting into a 4-day work week.
Moving from 5-Day Work Week to 4-Day Work Week
4,000 years ago, the Babylonians believed seven planets existed thus they believe working seven-day week will improve productivity.
It was only around one century ago, in 1908, the first five-day workweek was instituted by a New England mill in the United States to accommodate the Jewish workers who have to observe the Sabbath from sundown Friday to sundown Saturday.
Subsequently, companies adopt a 5-day work week with a full-time employee working for 38 to 40 hours a week.
“The earliest record of using the word “Weekend” is in 1879.”
The change of moving from a 7-day work week to a 5-day work week comes from the idea of a shorter workweek would lead to increased productivity, improved mental and physical health, and higher employee retention rates.
In recent years, there has been a rise in the idea of a four-day work week and it will probably be the future of work.
Proponents of the four-day work week argue that it would be more efficient for society as a whole and that it would allow people to have more time for themselves and their families and the results seem to speak for themselves.
Evolution of Four-Day Workweek
In 1930, economist John Maynard Keynes suggest with the developmental advancement of technology and productivity improvements, having a 15-hour workweek will be possible.
Two decades after, in 1956, US Vice President Richard Nixon suggest that Americans would only have to work four days per week in the not-too-distant future.
After 6 decades, in 2019, Microsoft Japan Co. initiated a 4-day work week trial for all their employees and the shortened workweek have resulted in a 40% increase in work productivity.
Encouraged by the results, attracted many companies and organization around the globe are implementing the new four-day workweek arrangement.
What Does 4-Day Work Week Mean To You?
Depending on contracts or workplace agreements, the reduced number of working days may or may not correspond to a salary reduction or reduced benefits.
For some companies, it comes down to a 100:80:100 ratio.
What is the 100:80:100 ratio?
The 100:80:100 ratio means that employees are able to retain 100 percent of their pay while reducing their work hours to 80%. However, they must retain 100% productivity.
The 100:80:100 ratio totally makes sense, and it benefits both the employee and the employer. Reduction of work hours does not necessarily mean reducing the amount of work, but reducing the unproductive hours at work and being more efficient at the task each employee does.
Research suggests in every 8-hour work day, the average employee is only productive for 2 hours and 53 minutes. The rest of the time is often used to perform unproductive tasks that do not contribute to the team or organization’s success.
Below are the top 10 unproductive activities an average employee spends at work.
| Unproductive activities at work | Time |
|---|---|
| Reading news online | 65 minutes |
| Checking social media | 44 minutes |
| Chatting with co-workers not related to work | 40 minutes |
| Searching for new jobs | 26 minutes |
| Taking smoke breaks | 23 minutes |
| Making non-work-related calls | 18 minutes |
| Making hot drinks | 17 minutes |
| Texting or instant messaging | 14 minutes |
| Eating snacks | 8 minutes |
| Making food in the office | 7 minutes |
With the data above we can conclude the following:
- 37% of the time an average employee spends at work is working on activities that make a difference in the team or organization’s success.
- 63% of the time an average employee spent at work is doing activities that are unproductive.

With companies adapting to a 4-day work week, employees simply have to reduce the amount of time spent on unproductive activities to ensure 100% of the work is done.
Join over 11,000+ achievers who are committed to achieving their career goals!






